June
26
2015
Big Data and Hadoop in Telecom Domain
Published by BIWHIZ team
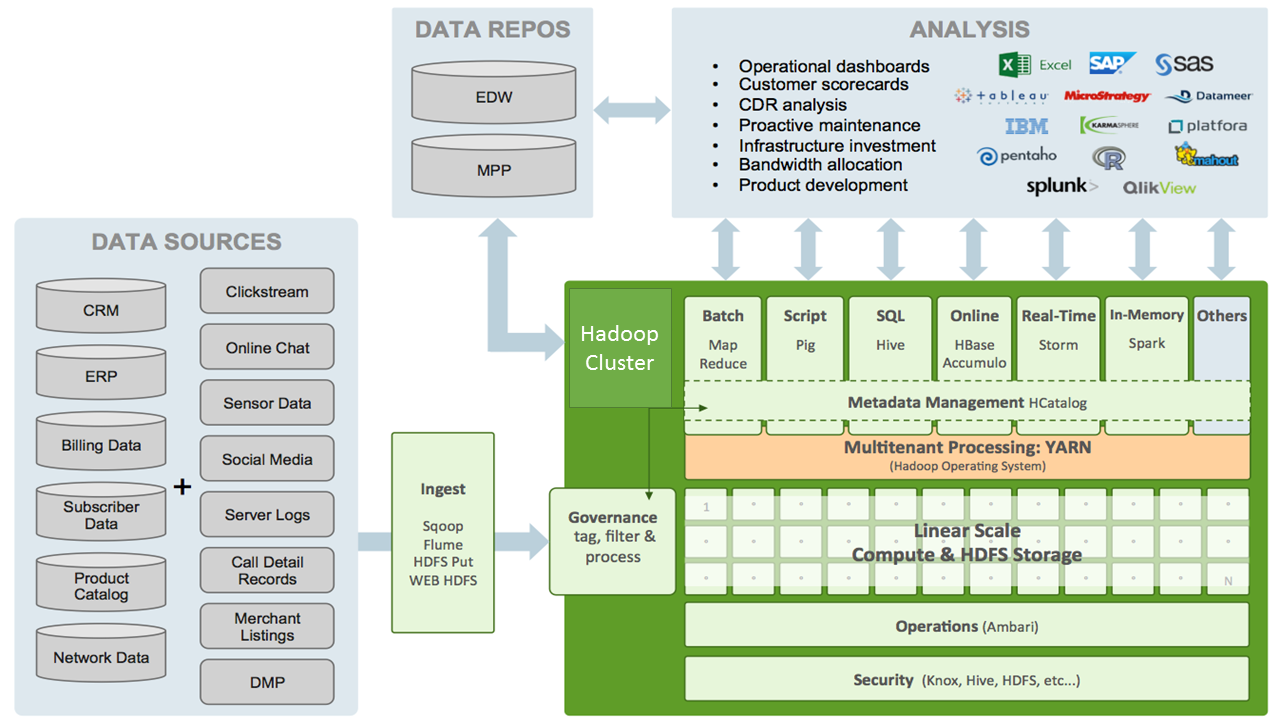
The rapid pace of telecommunications data growth requires more efficient, scalable storage. So telcos are using Apache Hadoop to turn their burgeoning storage liabilities into strategic information assets.
The following are some of the examples where Telcos are using big data to their advantage :-
- Analyze Call Detail Records (CDRs)
Telcos perform forensics on dropped calls and poor sound quality, but call detail records flow in at a rate of millions per second. This high volume makes pattern recognition and root cause analysis difficult, and often those need to happen in real-time, with a customer waiting for answers. Delay causes attrition and harms servicing margins.
Apache Flume can ingest millions of CDRs per second into Hadoop, while Apache Storm processes those in real-time and identifies any troubling patterns. HDP facilitates long-term data retention for root cause analysis, even years after the first issue. This CDR analysis can be used to continuously improve call quality, customer satisfaction and servicing margins. - Service Equipment Proactively
Transmission towers and their related connections form the spinal chord of a telecommunications network. Failure of a transmission tower can cause service degradation. Replacement of equipment is usually more expensive than repair. There exists an optimal schedule for maintenance: not too early, nor too late.
Hadoop stores unstructured, streaming, sensor data from the network. Telcos can derive optimal maintenance schedules by comparing real-time information with historical data. Machine learning algorithms can reduce both maintenance costs and service disruptions by fixing equipment before it breaks. - Rationalize Infrastructure Investments
Telecom marketing and capacity planning are correlated. Consumption of bandwidth and services can be out of sync with plans for new towers and transmission lines. This mismatch between infrastructure investments and the actual return on investment puts revenue at risk.
Network log data helps telcos understand service consumption in a particular state, county or neighborhood. They can then analyze network loads more intelligently (with data stretching over longer periods of time) and plan infrastructure investments with more precision and confidence. - Recommend Next Product to Buy (NPTB)
Telecom product portfolios are complex. Many cross-sell opportunities exist for the installed customer base, and sales associates use in-person or phone conversations to guess about NPTB recommendations, with little data to support their recommendations.
Hadoop gives a telco the ability to make confident NPTB recommendations, based on data from all of its customers. Confident NPTB recommendations empower sales associates (or self-service) and improve customer interactions. A Hadoop data lake reduces sales friction and creates NPTB competitive advantage similar to Amazon’s advantage in eCommerce. - Allocate Bandwidth in Real-Time
Certain applications hog bandwidth and can reduce service quality for others accessing the network. Network administrators cannot foresee the launch of new hyper-popular apps that cause spikes in bandwidth consumption and then slow performance. Operators must respond to bandwidth spikes quickly, to reallocate resources and maintain SLAs
Streaming data in Hadoop helps network operators visualize spikes in call center data and nimbly throttle bandwidth. Text-based sentiment analysis on call center notes can also help understand how these spikes impact customer experience. This insight helps maintain service quality and customer satisfaction, and also informs strategic planning to build smarter networks. - Develop New Products
Mobile devices produce huge amounts of data about how, why, when and where they are used. This data is extremely valuable for product managers, but its volume and variety make it difficult to ingest, store and analyze at scale. Not all data is stored for conversion into business insight. Even the data that is stored may not be retained for its entire useful life.
Apache Hadoop can put rich product-use data in the hands of product managers, which speeds product innovation. It can capture product insight specific to local geos and customer segments. Immediate big data feedback on product launches allows PMs to rescue failures and maximize blockbusters. - Operational Intelligence
Telcos can benefit from big data analytics by gaining a deeper understanding of switching, frequency utilization, and capacity use for capacity planning and management. Analyzing consumption of services and bandwidth in specific regions helps with planning locations for infrastructure investment. Capturing and analyzing data produced by the infrastructure and by sensors can accelerate troubleshooting information about the network. Hadoop can efficiently collect and store huge volumes of sensor data and scale as data grows. - Customer Churn Analysis
Accurate diagnosis of customer churn and enabling of alerts when a customer exhibits behavior that suggests imminent defection is a critical requirement for telcos. By looking at multiple factors, such as comments on social media and declining usage, along with historical data that show patterns of behavior that suggest churn, companies can predict when a customer is at risk of defecting. Hadoop helps bring together customer transaction data and communication streams from customers in real-time that can show how customers feel about their service. This is critical for detecting and addressing customer satisfaction issues in real time. - Fraud Detection
Hadoop need to protect their customers and their bottom line by proactively detecting fraudulent activities. They can analyze usage data, location-specific data and customer account data in real time to model baseline “normal” behavior. Hadoop provides can help build models that can flag anomalous phone calls that might indicate theft or hacking, both in business-to-business and business-to-consumer environments. - Clickstream Analysis
Communications service providers can generate more revenue and create better customer experiences by tracking and analyzing customer clickstreams to understand their preferences and propensity to buy. For example, if clickstreams show a customer has been researching specific products, the Hadoop can serve up targeted promotions or offers to that individual customer. They can optimize web pages to increase conversion including cross-sell opportunities. Hadoop helps ingests data faster, enables streaming writes to update models and target customers quicker. - Recommendations
Hadoop can make more accurate and relevant recommendations to customers in real time by analyzing customer call logs, usage and customer satisfaction data combined with social media data to understand customer preferences and behavior. These recommendations can include cross-selling new services, matching pricing plans, or making targeted offers for sports or music enthusiasts. Hadoop delivers real-time capabilities that enable recommendations to be delivered at just the right time and place. - Network Management/Optimization
Communications service providers can optimize quality of service and routing by being able to analyze network traffic in real time. This enables them to respond to fluctuations in traffic and reallocate bandwidth as needed. They can use Hadoop to identify and resolve network bottlenecks, manage capacity to plan for infrastructure investments and maintain quality of service, and optimize the network for their most valuable customers.


Comments
comments powered by Disqus